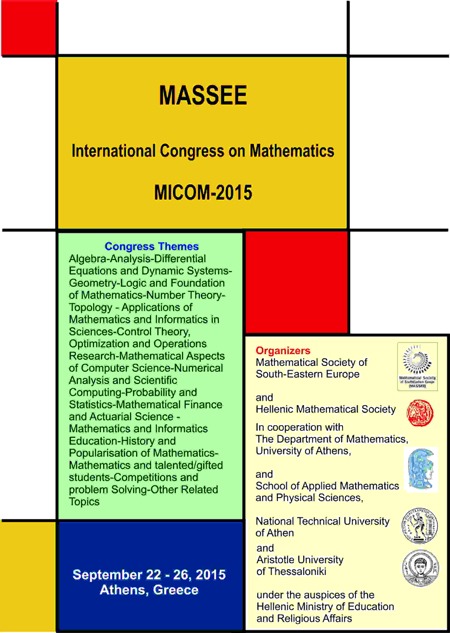
.
Επίκαιρα
Νέα
Δελτία Τύπου
Διοικητικό Συμβούλιο & ΕΕ
Εκδόσεις





Νέα Παραρτημάτων
Διεθνείς Διοργανώσεις
- All
- CGM
- JBMO
- BMO
- MICOM